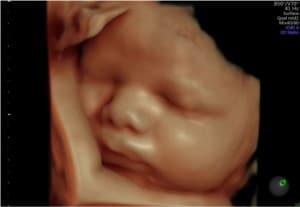
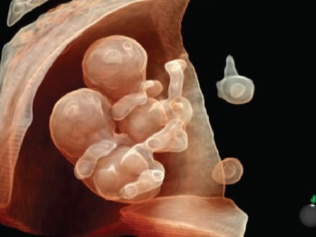
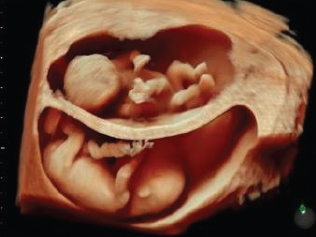
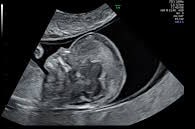
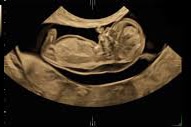
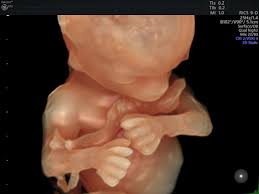
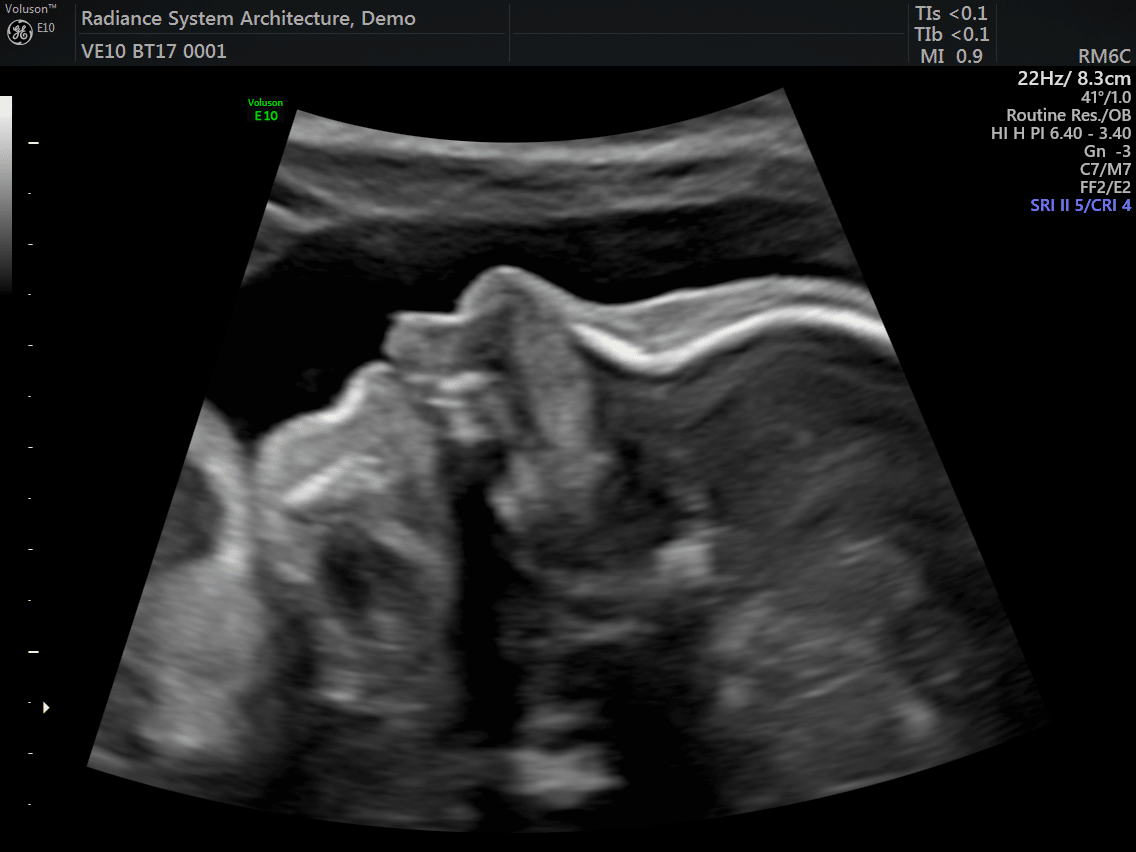
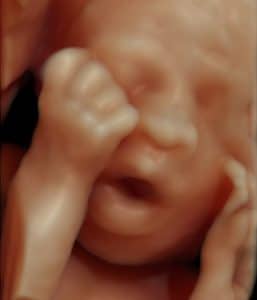
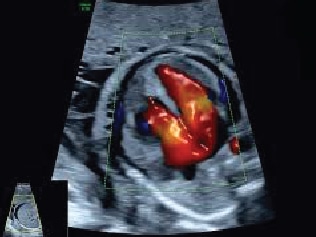
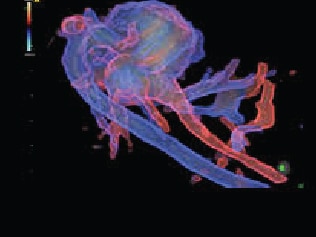
Being one of the most recent and impactful innovations in the domain of prenatal diagnosis, 5D HD Live Silhouette and HD Live Studio ultrasounds are recommended in a routine application for gestation monitoring. Two aspects should be underlined: On one hand, it provides real-time 3D images instead of flat 2D images, contributing to the accuracy of the diagnosis; on the other hand, it has been demonstrated that such images further strengthen the bond between mother and child even before delivery.
It is particularly remarkable, with regards to 5D HD Live Silhouette and HD Live Studio ultrasounds, that the resulting images allow parents to establish a strong bond with their offspring. Parents actually see and understand what their offspring looks like. This strong bond has been proven by psychological research involving the impact before and after 2D, 5D HD Live Silhouette and HD Live Studio ultrasounds..
In certain cases, where a fetal pathology exists, 5D HD Live Silhouette and HD Live Studio ultrasounds are particularly useful for the explanation of some malformations, such as facial ones, since the parents are able to watch the alteration in a clear and understandable way. The possibility of using the 3 planes of space helps to complement the malformation diagnosis and provide better detection of otherwise non diagnosable alterations. This aspect is indeed distinctively important from the point of view of the concrete malformation diagnosis of the baby and his or her future quality of life.
Additionally, a number of European studies show that the use of 5D HD Silhouette and HD Live Studio ultrasounds has enabled a deeper understanding of the development of fetal movement and behavior, previously unknown. It has been discovered that fetuses may open their eyes after 18 weeks. It has also been observed that the little ones laugh, cry, scratch and use their mouths in a sucking fashion after 26 weeks of gestation. All these complex functions require vital neurological development.
5D HD Live Silhouette and HD Live Studio ultrasound is a powerful working tool granting a deeper understanding and interpretation of human behavior during the fetal stage. The clarity and high resolution of the images further improves the capacity of the abnormality diagnosis. It allows us to have an idea of what the child is going to be like before his or her birth.